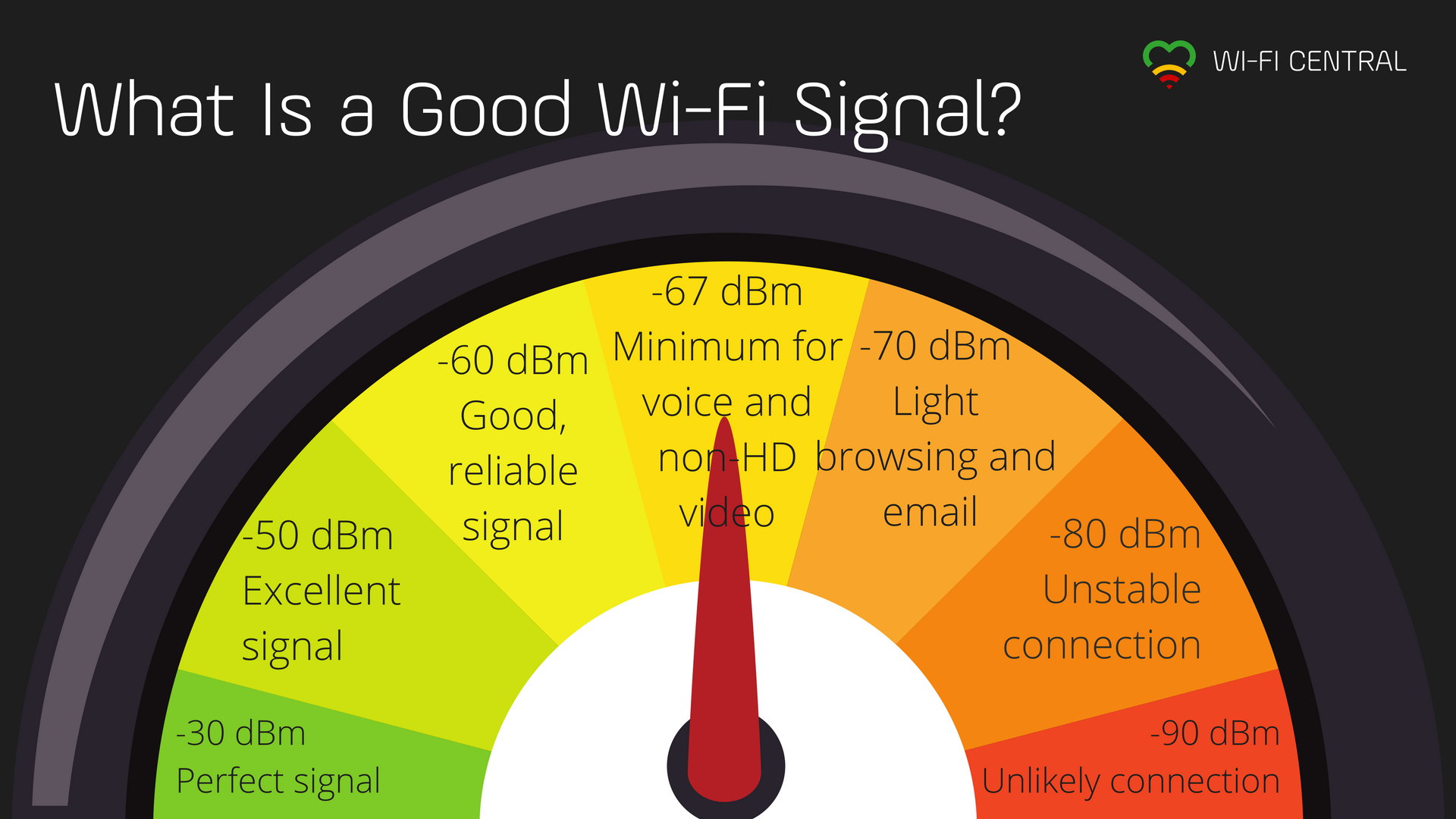
A quick overview of the required Wi-Fi signal strength for different online activities.
Talking about “good signal strength” may have become part of everyday language, but what constitutes a good Wi-Fi signal, really? Do you know what it takes to be able to use demanding services like Netflix and videoconferencing over Wi-Fi?
Signal strength is measured in dBm or decibel milliwatts, which, somewhat confusingly, is expressed only in negative values (with a minus sign in front).
So what are the good and acceptable dBm values for wireless internet?
Here is what the Wi-Fi signal strength values mean
| Signal strength | Quality to expect | Required for |
|---|---|---|
| -30 dBm | Maximum signal strength, you are probably standing right next to the access point / router. | |
| -50 dBm | Anything down to this level can be regarded as excellent signal strength. | |
| -60 dBm | This is still good, reliable signal strength. | |
| -67 dBm | This is the minimum value for all services that require smooth and reliable data traffic. | VoIP/VoWi-Fi Video streaming/streaming (not the highest quality) |
| -70 dBm | The signal is not very strong, but mostly sufficient. | Web, email, and the like |
| -80 dBm | Minimum value required to make a connection. You cannot count on a reliable connection or sufficient signal strength to use services at this level. | |
| -90 dBm | It is very unlikely that you will be able to connect or make use of any services with this signal strength. |
How to measure the received signal strength
To measure signal strength at a given location and time, you can use a Wi-Fi scanner. You can read more about this in our article How to find good Wi-Fi channels and bad neighbors.
The measurement you are looking for is RSSI, which is short for received signal strength indicator.
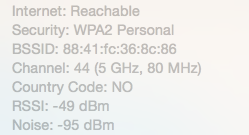
If you are running Mac OS X, you can also measure the received signal strength directly without installing anything: Hold down the Altkey and click the Wi-Fi icon in the top menu, and details of communication with the wireless access point will appear under the name of the active Wi-Fi network.
If you would like to map out the signal for an entire home, we recommend using a heat mapper to create a heat map of good and bad coverage zones. See also: Map your wireless network with a heat mapper.
Poor signal strength? Remove obstacles
Have you done your testing and concluded that the signal strength is insufficient? First of all:
Don’t be tempted to try to amplify the transmit strength from your router / access point. You may sabotage both yourself and your neighbors in the process, and you risk breaking the law along the way. Read more about this in Don’t. Boost. Your Wi-Fi Signal.
Of course, the performance and capacity of the wireless network depends on more than the signal emitted from the access point, but the most important thing you can do for the signal is:
- Move the router or other access point high up and in front of any obstacles. Preferably high up on the wall.
- Place your devices and access points with as much of a clear line of sight between them as possible.
Get further advice on what you can do yourself to improve your home Wi-Fi in: Better Wi-Fi at Home: 18 Free Tips.
Article by Jan Pedro Tumusok and Jorunn Danielsen