Wifi band steering detects what a wireless device supports and automatically steers it to the best available frequency band when connecting to a wifi network.
Band steering is functionality that automatically steers anyone connecting to a wireless network to the best frequency band available and supported, thereby optimizing performance for the client.
What Are Frequency Bands?
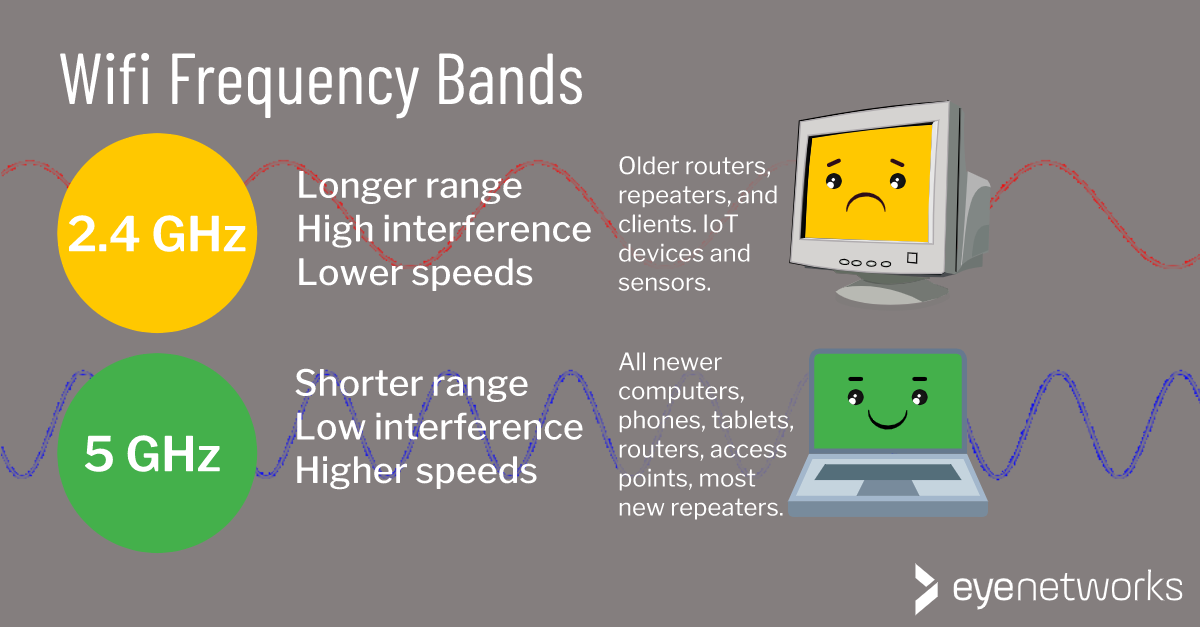
A frequency band is a section of a lager frequency area. Wireless internet connections–wifi–operate on three frequency bands:
- 2.4 GHz is the frequency band used by the older wireless technologies (802.11 b/g/n), and in practice it is the slowest network. Because of the long reach of its signals, this frequency band is also the most vulnerable to interference from other Wi-Fi networks, as well as other wireless equipment (Bluetooth, baby monitors), and microwave ovens. See also 10 things that interfere with and block Wi-Fi signals.
- 5 GHz is the frequency band used by Wi-Fi 5 and 6, as well as some older standards (802.11 a/n), and it provides higher speeds/better performance. Because of the shorter reach of the signals on this frequency band, multiple access points are often necessary to provide satisfactory coverage in a home.
- 6 GHz is the newest frequency band , which is only used by Wi-Fi 6E and 7. Not many networks or clients support this frequency band yet, but the number is growing.
What Happens When You Don’t Have Band Steering?
If your equipment does not support band steering, it is up to the user or the device to select the correct/best frequency band. Many routers are set up by the manufacturer or internet provider so that you have separate networks with separate names for each frequency band, and then it is up to the user to know which network and thus which band to connect to.
Worst case, the user tries to connect to a network that is not supported by the device, or a network that provides much slower performance than the device actually supports.
See also Five Reasons Bot to Buy a Wi-Fi repeater.
What Does Band Steering Do?
Band steering means you don’t have to worry about which frequency band is supported by the different computers and devices that you use, because you have a router or other wireless access point that can make these assessments and direct each device to the appropriate frequency band.
Band steering is often part of a more comprehensive functionality called client steering, which ensures that all clients (devices) connect to the wireless access point that provides the best performance.
Article by Geir Arne Rimala and Jorunn Danielsen